Have you ever walked into a store planning to buy just one thing and walked out with a cart full of items? Or maybe you’ve gone to a restaurant for a quick bite and ended up settling for a full meal and even got a takeout to eat later? You probably have been there before.
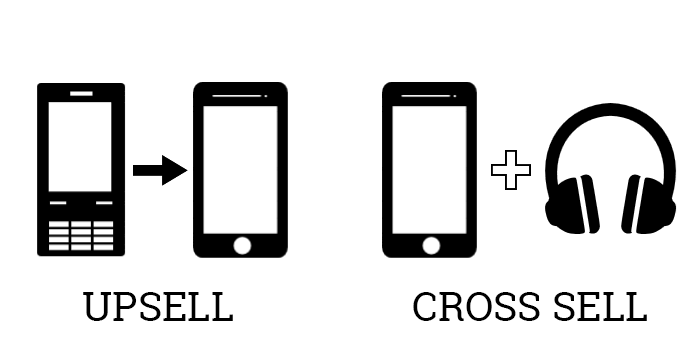
That sales technique of persuading customers to spend more has a name: upselling.
Think of it as the art of persuading customers to purchase a higher-priced or upgraded version of a product or service they’re already interested in. Think of it as offering an irresistible deal that meets and exceeds their initial expectations.
In this article, I’ll explore the basics of upselling and how it can be implemented effectively in e-commerce.
What is Upselling In Ecommerce?
In the context of e-commerce, upselling is a strategic sales technique that aims to increase the value of a customer’s purchase by offering them additional products or upgrades that complement their original purchase.
For example, when a customer adds a small cup of coffee to their online shopping cart, the e-commerce website suggests adding a larger cup at a discounted price. The recommendation is strategically placed during the checkout process, enticing the customer to consider the upgrade and potentially increase their order value.
It’s like adding that extra sprinkle of goodness to their shopping experience. Instead of just settling for the initial purchase, you seize the opportunity to offer customers something extra that enhances their overall satisfaction and brings them even more value.
Upselling is not about pressuring customers or making them feel they’ve made the wrong choice. It’s about presenting them with valuable options they may not have considered initially.
Real-Life Examples of Upselling
-
Apple’s iPhone Storage Upgrade
When purchasing an iPhone, Apple offers various storage options. The base model has a lower storage capacity, but Apple upsells customers by offering higher storage versions for an additional cost.

For example, instead of buying the 64GB model, Apple encourages customers to upgrade to the 256GB or 512GB version. This upsell not only increases the value of the sale but also appeals to customers who want more storage for their apps, photos, and videos.
-
Starbucks’ Upsell on Drink Sizes

A classic example of upselling happens at Starbucks when the barista asks, “Would you like to make that a venti?” Customers who order a small (tall) coffee are encouraged to upgrade to a larger size (grande or venti) for a slightly higher price.
This simple upsell tactic significantly increases the average order value while offering more value to the customer.
-
Amazon’s Upsell with Product Versions
On Amazon, when customers view a product, such as an electronic device or household item, they are often shown an upgraded version.
For example, when browsing for a basic coffee maker, Amazon may suggest a higher-end model with additional features like a built-in grinder or programmable settings.
This upsell encourages customers to consider a more advanced and often more expensive version of the product they were initially interested in.
-
McDonald’s “Go Large” Option
McDonald’s also employs a successful upselling tactic with their “Go Large” option. When customers order a burger, the cashier often asks if they want to upgrade their order to add fries, drinks, etc for a small additional charge.

This simple upsell increases the overall order value while offering the customer a larger portion, creating a win-win scenario for both the business and the customer.
What is Cross-selling In Ecommerce?
Cross-selling is an e-commerce sales strategy that often complements upselling to maximize customer value.
Unlike upselling, which aims to get the customer to purchase a higher-end version of a product, cross-selling focuses on recommending related or complementary items that enhance the customer’s original purchase.
For example, if a customer buys a laptop, a cross-sell would suggest a laptop bag, external mouse, or antivirus software. These recommendations aim to increase the overall value of the purchase by encouraging customers to add items that complete their experience.
Cross-selling provides convenience by bundling products that naturally go together, saving customers time and helping them make more informed buying decisions.
When done well, it doesn’t feel like an additional sale—it feels like a thoughtful recommendation.
Examples of Cross-selling Strategies
Let’s look at some real-life applications of upselling and its impact on businesses.
-
McDonald’s Meal Combo: “Would You Like Fries With That?”
A lot of people are familiar with the famous McDonald’s upsell catchphrase.
“Would you like fries with that”
It represents a classic example of suggestive selling, where the restaurant employee suggests adding a side of fries to a customer’s order.
The phrase is used during the ordering process when a customer selects a main item, such as a burger or sandwich. The employee then asks if the customer would like to add fries to their order, implying that the meal would be more satisfying or complete by adding this side item.
This upselling technique is effective for several reasons. First, fries are a trendy and iconic item on McDonald’s menu, making them a natural choice to suggest.
Second, the phrase is simple, direct, and easy to understand, requiring minimal effort from the employee and customer.
According to a study, this simple phrase accounts for 15-40% of McDonald’s annual revenue.
-
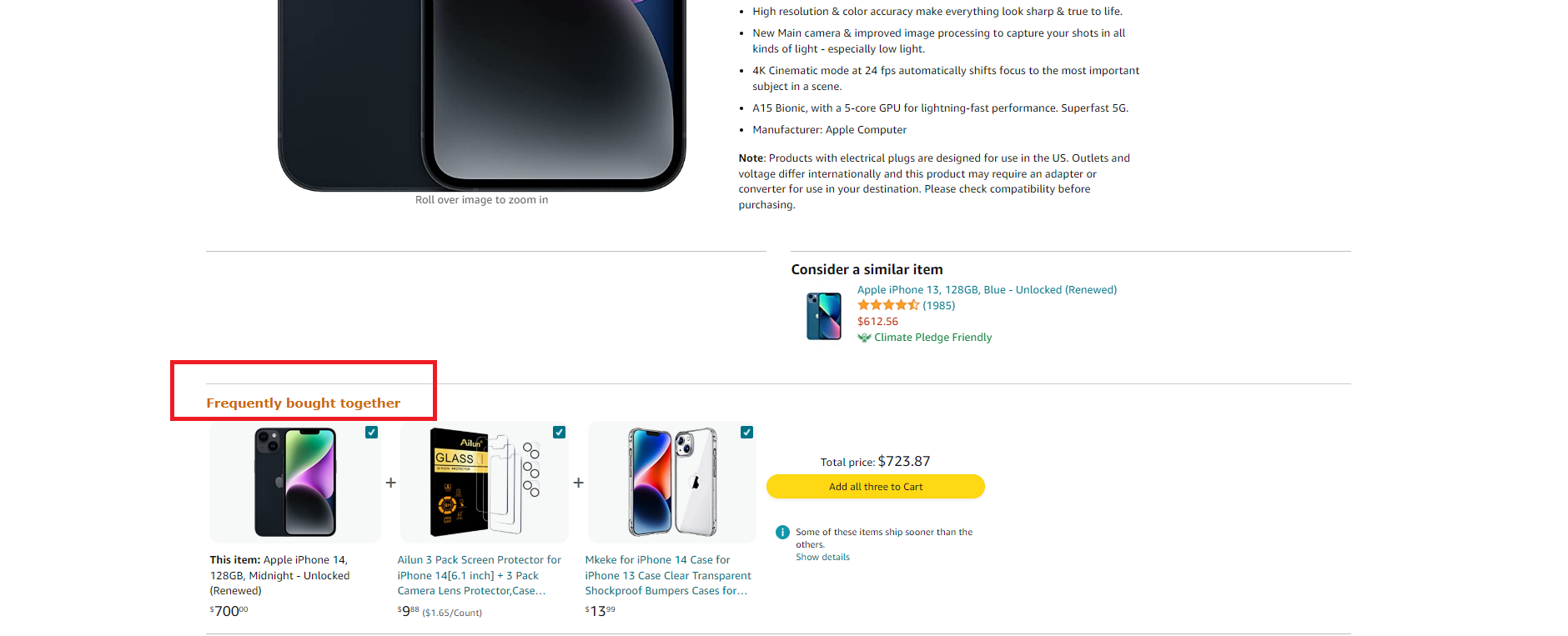
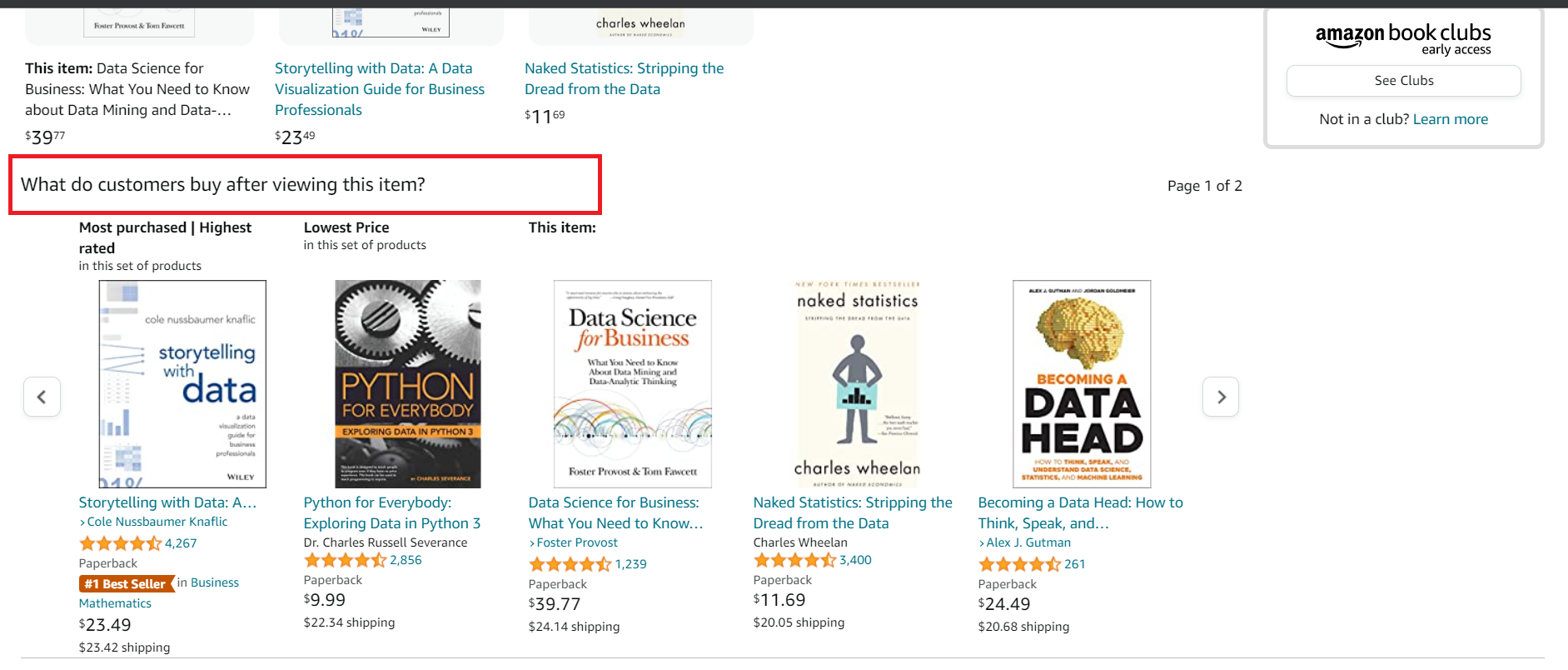
Amazon’s “Frequently Bought Together” and “Customers Who Bought This Also Bought”
On product pages, Amazon displays sections that showcase items frequently bought together or products that customers commonly purchase with the selected item.
These recommendations not only expose customers to additional options but also create a sense of social proof, as they are based on the buying patterns of other shoppers.
The then-CEO of Amazon, Jeff Bezos, revealed that 35% of sales on the Ecommerce platform were due to cross-selling and upselling.
Upselling vs. Cross-selling: What’s the difference?
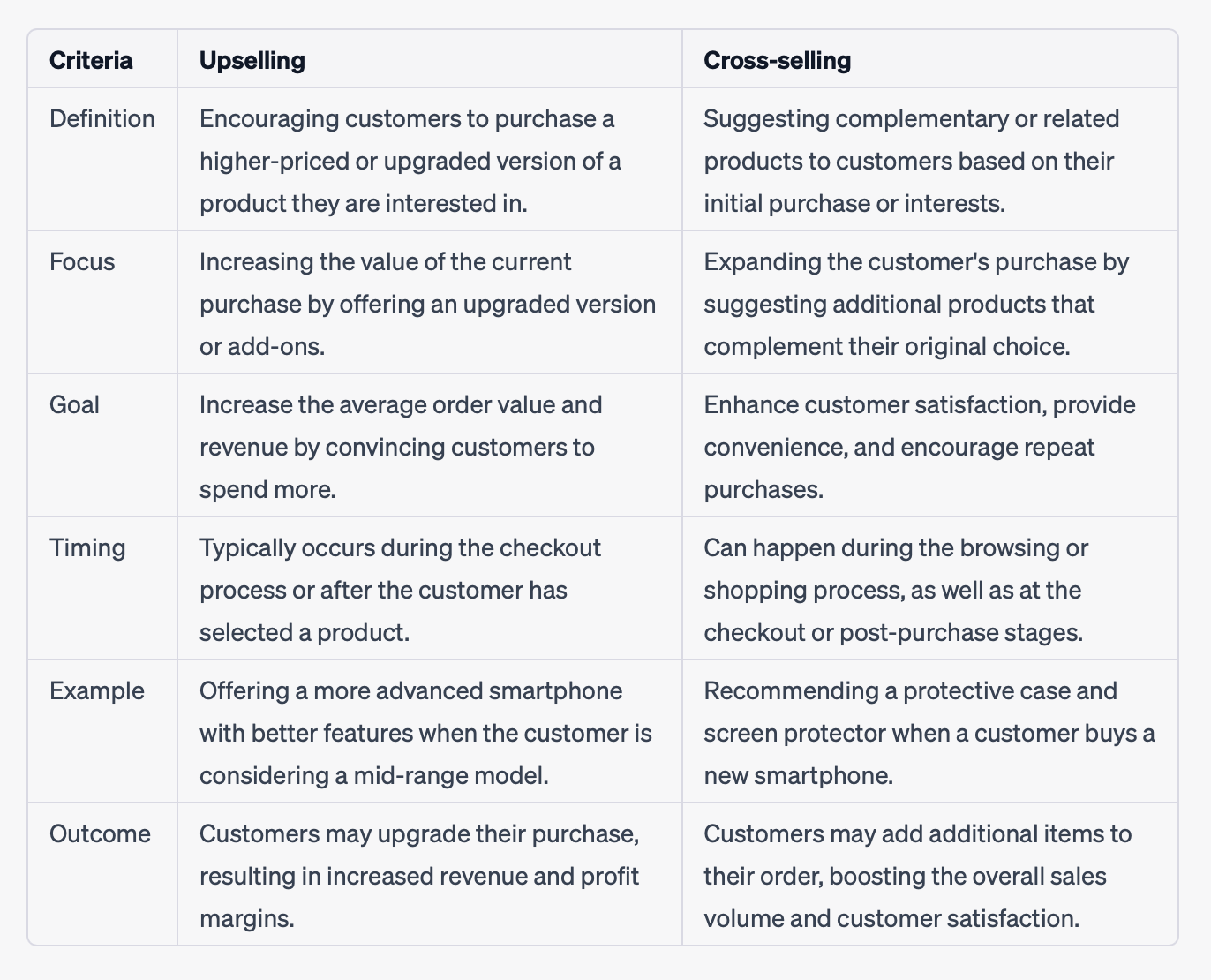
As we’ve discussed, upselling is a sales technique that involves offering existing customers a higher-end or more advanced version of the product they are considering or have already chosen.
On the other hand, cross-selling focuses on suggesting complementary or related products to the one a customer is considering or has already purchased. It’s about identifying items that complement their original choice, enhance their experience, or fulfill additional needs.
Cross-selling aims to expand the customer’s purchase by offering them products that complement their initial selection. In a zoomed-in view, you can tell that ecommerce businesses use both upselling and cross-selling sales techniques to increase the average order value as well as the customer lifetime value.
Simply put, upselling encourages customers to “go up” or upgrade their purchase while cross-selling encourages them to “go across” and consider related or complementary products.
Benefits of Upselling and Cross-Selling
Why is upselling such a game-changer in the world of e-commerce?
Here are some key benefits and the potential impact of implementing effective upselling strategies in your e-commerce business:
-
Increased Average Order Value (AOV)
Both upselling and cross-selling can significantly boost your AOV. Upselling encourages customers to purchase higher-priced or upgraded products, while cross-selling introduces them to complementary items that enhance their initial purchase.
For example, when a customer buys a laptop, you can upsell them to a version with more RAM and cross-sell accessories like a mouse or laptop bag, resulting in a higher overall order value.
-
Enhanced Customer Experience
Offering personalized upsell and cross-sell recommendations shows that you understand your customer’s needs and are focused on improving their shopping experience.
Customers feel that their purchase is more complete when functional upgrades or related products are suggested—like upselling a camera with a lens kit or cross-selling a memory card.
This personalized touch builds trust, increases satisfaction, and encourages repeat business.
-
Improved Customer Retention and Loyalty
Consistently offering valuable recommendations through upselling and cross-selling can foster long-term customer relationships.
Enhancing the customer experience with thoughtful product suggestions and upgrades builds loyalty and encourages customers to return. These strategies show that you’re focused on their needs, not just making a sale.
-
A Tool for Customer Education
Both upselling and cross-selling serve as educational tools by informing customers about the full range of products or services available.
For instance, a subscription service can upsell customers to a premium plan with additional features, while cross-selling can introduce them to complementary solutions that save time or improve functionality.
This approach increases sales and deepens customers’ understanding of your offerings.
-
Increased Profit Margins
Both upselling and cross-selling contribute to higher profit margins without the need for additional customer acquisition costs.
By selling higher-end products or complementary items, you’re maximizing the value of each transaction. For example, upselling customers from a basic phone to a premium model with more features often generates a higher profit margin.
Similarly, cross-selling accessories like headphones or chargers, which are typically marked up, can also improve your profit per sale.
Overcoming Challenges Associated With Upselling and Cross-selling.
Both upselling and cross-selling come with their own set of challenges, and it’s important to understand how to navigate these to ensure a positive customer experience. Here’s how to avoid common pitfalls and implement these strategies effectively.
-
Balancing Customer Experience
The key to successful upselling and cross-selling is enhancing the customer’s experience, not overwhelming them.
Pushing too many recommendations can feel intrusive, whether it’s a suggestion to upgrade or to buy additional items.
The goal is to present these offers in a way that feels helpful, not pushy, ensuring that customers leave with a positive experience and not a sense of being pressured.
-
Pricing and Value Perception
Customers need to feel that the extra cost, whether for an upsell or a cross-sell, is worth it.
When upselling, it’s necessary to communicate how an upgraded product adds value—whether through better features, improved functionality, or long-term savings.
For cross-selling, emphasize how complementary products improve the use or enjoyment of the original purchase.
Tiered pricing strategies or bundling-related items can make offers more attractive and help justify the additional spending.
Always ensure that the value of the offer is transparent to the customer so they perceive the recommendation as beneficial rather than just an attempt to upsell or cross-sell for the sake of it.
-
Avoid Overwhelming Customers
It’s easy to overwhelm customers with too many options, leading to decision fatigue or even cart abandonment.
The solution is to limit the number of upsell or cross-sell suggestions.
Focus on one or two highly relevant recommendations that genuinely improve their purchase experience.
For example, if a customer purchases a phone, an appropriate cross-sell could be a protective case, and a well-timed upsell could be a model with more storage.
The right offer, delivered at the right time, feels less like a sales tactic and more like a valuable suggestion.
Over To You!
Upselling and cross-selling are powerful strategies for driving revenue and maximizing customer value.
Businesses can significantly increase their average order value without acquiring new customers by encouraging customers to consider higher-priced or complementary options.
These strategies boost revenue and enhance the overall customer experience by offering personalized and relevant product suggestions.
Upselling and Cross-Selling FAQs
What is upselling and cross-selling?
Upselling is the strategy of encouraging customers to buy a more expensive version or add premium features to the product they are already interested in. The goal is to increase the value of the transaction while providing the customer with a better option that suits their needs.
Cross-selling, on the other hand, involves suggesting additional or complementary products that go well with the original purchase. For example, if a customer buys a laptop, offering a mouse, laptop bag, or extended warranty would be cross-selling. Both techniques aim to maximize the customer’s spend while enhancing their experience with useful suggestions.
What is an example of cross-selling?
An example of cross-selling could occur in an online clothing store. If a customer adds a shirt to their cart, the store might suggest a matching pair of pants, shoes, or accessories, such as a belt or scarf, that complement the shirt. By offering related products, the retailer enhances the shopping experience and increases the likelihood of a larger purchase.
What is an example of upselling?
Upselling happens when a business encourages a customer to buy a higher-tier product or service. For example, in a car dealership, a customer looking at a base model might be encouraged to consider a model with premium features such as leather seats, a sunroof, or advanced safety technology. The idea is to convince the customer to see the added value of upgrading to a more expensive option, ultimately benefiting both the customer and the business.