A/B testing is a powerful tool for optimizing products and improving the user experience.
By comparing the performance of two different product versions, you can determine which version is most effective at achieving your business goals.
However, A/B testing requires a systematic and careful approach to get reliable and meaningful results.
This step-by-step guide will walk you through the process of conducting an A/B test, from defining your goals and objectives to analyzing and interpreting the results.
By following these steps, you can use A/B testing to make data-driven decisions and continuously improve your product’s performance and user experience.
What is A/B Testing?
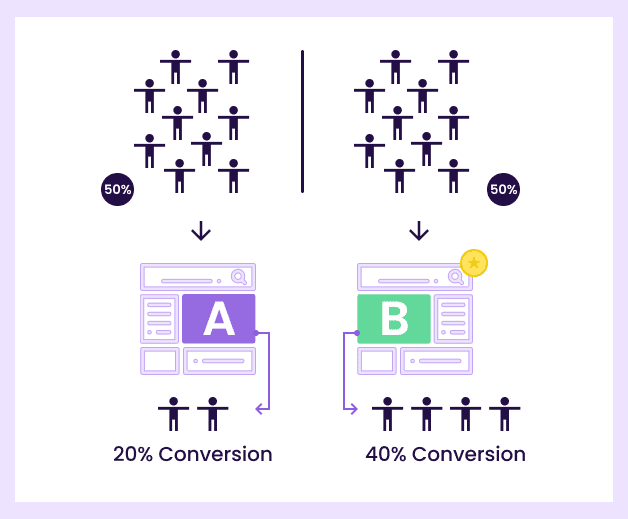
A/B testing, also known as split testing, is an experimentation method that compares different versions of a webpage or marketing ad campaign to see which performs better and is more effective in achieving specific business goals.
It is called A/B testing because there are typically different versions of a webpage being compared against each other. Where A can be the original version and B is a challenger version.
A/B testing has different categories, which include the following:
1. Element level testing: This is considered the easiest category of A/B tests because you only test website elements like images, CTAs, or headlines. This testing aims to create a hypothesis as to why the website elements need to change.
2. Page-level testing: As the name suggests, this testing involves moving elements around a page or removing and introducing new elements.
3. Visitor flow testing: This category of split test involves testing how to optimize visitors’ navigation of your site. Visitor flow testing is usually directly related to the impact on conversion rate.
4. Messaging: Yes, you have to A/B test the messaging on different sections of your site to ensure consistency in tone and language. Messaging A/B tests take a lot of time since you have to check every page and element for messaging consistency.
5. Element emphasis: Sometimes, in an attempt to reinforce an element, such as a button, headline, or CTA, we may repeat such elements too many times. This category of A/B testing focuses on answering questions like “How many times should an element be displayed on a page or throughout the website to get visitors’ attention?”
Benefits of A/B testing
The benefits of A/B testing are well documented. Here are ten advantages of running A/B tests:
- Improved effectiveness: A/B testing allows you to test different product variations and compare their performance to determine which version is most effective at achieving your business goals.
- Enhanced user experience: A/B testing allows you to test different design or feature changes and see how they impact user behavior, so you can optimize the product to better meet the needs and preferences of your users.
- Data-driven decision-making: A/B testing allows you to make decisions based on objective data rather than subjective opinions or assumptions, which can help you more effectively optimize the product.
- Improved conversions: A/B testing can help you identify changes that increase conversions, such as increasing the effectiveness of calls to action or improving the product’s overall usability.
- Increased customer retention: A/B testing can help you identify changes that improve customer retention, such as reducing friction in the user experience or making it easier for customers to complete tasks.
- Greater efficiency: A/B testing can help you identify changes that make the product more efficient, such as streamlining processes or reducing the number of steps required to complete a task.
- Enhanced engagement: A/B testing can help you identify changes that increase engagement, such as adding social media integration or improving the product’s overall design.
- Improved ROI: A/B testing can help you achieve a better return on investment by identifying changes that will enhance the product’s effectiveness and efficiency.
- Enhanced competitiveness: A/B testing allows you to continuously optimize and improve your product, which can help you stay competitive in a crowded market.
- Greater customer satisfaction: By using A/B testing to improve your product’s effectiveness and user experience, you can increase customer satisfaction and build loyalty.
When to Do A/B Testing
When should you use A/B testing? Well, there is never a wrong time for A/B testing. You should constantly be testing to identify opportunities for growth and improvement.
There are several situations in which A/B testing may be useful:
- When you want to test a new feature or design change: A/B testing allows you to compare the performance of your product/website with and without the new feature or design change, so you can see whether it has a positive or negative impact on user behavior.
- When you want to optimize a website for a specific goal, A/B testing allows you to test different variations of a website page to see which one performs best in achieving that goal, such as increasing conversions or improving user retention.
- When making data-driven decisions, A/B testing allows you to test different product variations and compare their performance based on objective data rather than relying on subjective opinions or assumptions.
It’s important to note that A/B testing should be part of a larger optimization process and is not a one-time activity.
It is often used in conjunction with other conversion rate optimization techniques.
How To Implement an A/B Test?
If you want to run tests, you will need the following:
A testing tool
Choosing the right A/B testing tool is a fundamental first step. The market offers a variety of options, each with different features and levels of complexity.
Some tools are designed for beginners and offer user-friendly interfaces, while others are more advanced and provide in-depth analytics and customization options.
FigPii, for instance, is a versatile tool that allows you to launch A/B tests easily and offers comprehensive tracking and analysis features.
When selecting a tool, consider factors such as your team’s technical expertise, the scale of your testing needs, and the specific functionalities that are most important to your business.
Test Hypothesis
Developing a clear test hypothesis is an important component of A/B testing. Start by identifying the specific changes you want to test, such as altering the layout of a webpage, changing the color of a call-to-action button, or modifying the copy of a headline.
Your hypothesis should include a prediction of how these changes will impact user behavior. For example, you might hypothesize that changing the call-to-action button from blue to red will increase the click-through rate by 10%.
A well-defined hypothesis helps guide your testing process and ensures your efforts align with your business objectives. It also provides a benchmark against which you can measure the success of your test.
Test variations
The next step is creating test variations. This involves designing multiple versions of the element you are testing. The control group represents the original version, while the treatment group includes the proposed changes.
For instance, if you’re testing a new headline for a landing page, the control group would see the current headline and the treatment group would see the new headline.
It’s important to ensure that the variations are significant enough to impact user behavior potentially. Subtle changes might not produce noticeable results, so aim for clear and distinct differences between your control and treatment groups.
Identify Goals and Metrics
Clearly define what you want to achieve with your A/B test. Choose primary and secondary metrics to measure its success.
These could include conversion rates, click-through rates, bounce rates, or other relevant KPIs. Having clear goals helps you evaluate the effectiveness of the changes and provides a focused direction for your analysis.
Website Traffic
Ensuring adequate website traffic is needed to achieve statistically significant results. Your website or application needs a sufficient volume of visitors to provide reliable data.
You may need to adjust the traffic allocation between the control and treatment groups to ensure each group receives enough visitors for the test to be valid.
For example, a 50/50 split is common, but depending on your traffic levels, you might choose a different ratio.
High traffic volumes enable quicker results, but if your site has lower traffic, you may need to run the test for a longer period to gather enough data.
Sample Size and Duration
Determine the appropriate sample size and duration for your test. This ensures that your results are statistically significant and not due to random chance.
Use sample size calculators if needed and consider running tests for a period that accounts for variations in user behavior over time.

Generally, tests should run for at least one full business cycle to account for variations in user behavior. For websites with lower traffic, this might mean running the test for several weeks or even months.
Be patient and resist the urge to end the test early, as doing so can lead to inaccurate conclusions. The goal is to reach a point where the data clearly indicates whether the changes are effective.
Tracking and Analytics Tool
Setting up accurate tracking and analytics is vital for measuring the success of your A/B test.
Identify the key metrics that will indicate whether your hypothesis is correct. These metrics could include conversion rates, bounce rates, average time on site, click-through rates, and other relevant data points.
Comprehensive analytics tools like Google Analytics will help you collect and analyze this data, providing insights into how users interact with your variations.
It’s important to ensure that your tracking mechanisms are correctly implemented to avoid any data discrepancies that could affect your results.
Quality Assurance (QA)
Perform quality assurance before launching your test to ensure it is set up correctly. This involves checking for any issues with the test setup, such as incorrect targeting or tracking of metrics, and ensuring the test does not disrupt the user experience. Quality assurance helps you avoid problems that could compromise the reliability of your test results.
Running the Test
Launch your test once everything is set up. Monitor the test closely to ensure data is being collected correctly and there are no technical issues. Make sure the test runs for the predetermined duration to gather enough data for analysis. This stage involves executing the planned A/B test and collecting data on user interactions with the test variations.
Analyze the Results
After the test, analyze the data to determine the effectiveness of the changes. Look for statistically significant differences between the control and treatment groups.
Consider both quantitative metrics and qualitative insights to understand user behavior and preferences. Accurate analysis of the results helps you identify the winning variation and understand why it performed better.
Implementing Changes
Based on the analysis, decide whether to implement the changes. If the test results are positive, apply the winning variation to your website or application.
This involves updating the live environment to reflect the successful changes tested. Ensure that all stakeholders know the results and the rationale behind the changes.
However, it’s important to recognize that failed experiments are also valuable learning opportunities. When a test does not produce the expected results, it offers insights into what does not work for your audience, which is just as important as knowing what does work.
Analyzing these outcomes can reveal underlying issues or new hypotheses that you hadn’t considered initially.
Document the findings from failed tests to understand why the changes did not meet expectations, and use this information to refine future experiments.
Document and Iterate
Document the results and insights gained from the A/B test. Use this documentation to inform future tests and continuous optimization efforts.
A/B testing is an iterative process, and ongoing experimentation helps you continually improve your user experience and conversion rates.
Documenting and iterating on the process ensures that you build on your successes and learn from each test to refine your approach over time.
With these elements in place, you can launch an A/B test and start gathering data to help you make informed decisions about the changes you want to make to your website or application.
What Can You A/B Test: 12 A/B Testing Examples
Instead of testing elements such as button sizes, color and font-styles, you should focus on high quality tests that drive conversions. Here are AB testing examples you should launch on your website:
1. Navigation menus
Experiment with different navigation menus to determine which ones are more intuitive and user-friendly for your visitors.
For instance, you could test a traditional dropdown menu against a hamburger menu. Consider also testing different placements for the navigation menu, such as at the top of the page versus a side panel.
When you analyze metrics like click-through rates, bounce rates, and time spent on pages, you can identify which navigation style helps visitors find what they’re looking for more efficiently and improves overall user experience.
2. Social proof
Incorporating social proof elements, such as customer reviews or ratings, can significantly affect conversions. For example, test the impact of a five-star rating system compared to a text-based review system.
Additionally, you could test the placement of these elements, such as including them near the product description versus placing them in a dedicated reviews section.
This can help you understand which format and placement are more effective in building trust and encouraging potential customers to take action.
3. Pricing
Test various pricing strategies to see which ones generate the most revenue. For instance, compare a discount off the regular price with a bundle deal.
You can also experiment with displaying pricing differently, such as showing the original price with a strikethrough next to the discounted price or testing the effectiveness of limited-time offers.
Analyzing the results will help you determine which strategy and presentation are more effective in incentivizing purchases and maximizing revenue.
4. Content length
Experiment with different content lengths to see which generates the most engagement or conversions. For example, test a short product description against a longer, more detailed one.
You might also consider testing different types of content, such as including bullet points versus paragraphs or adding supplementary content like videos or infographics.
This can reveal whether your audience prefers concise information, detailed content, or a mix of different content types, helping you optimize your approach.
5. Pop-ups
Test different pop-up designs and timings to identify the most effective way to generate leads or conversions.
A good example is comparing a pop-up that appears immediately upon page load with one that appears after a visitor has spent a certain amount of time on the page. You could also test different pop-up triggers, such as exit-intent pop-ups versus scroll-based pop-ups.
This can help you understand which approach is more effective in capturing visitor attention without being intrusive and which trigger works best for your audience.
6. Headlines
Headlines play a significant role in grabbing attention and driving conversions. Test different headline styles to see which ones generate the most clicks or conversions.
For instance, compare a straightforward headline with a more creative or attention-grabbing one. Additionally, you might test headlines with different emotional appeals, such as urgency, curiosity, or exclusivity.
This will help you determine which headline approach resonates best with your audience and encourages them to engage with your content.
7. Images
Visuals can greatly influence user engagement and conversions. Test different images to see which ones are more effective.
For example, compare a product photo with a lifestyle image that shows the product in use. You could also test the use of images featuring people versus those that focus solely on the product.
Experimenting with image placement, size, and style can help you determine which type of imagery better showcases your product and appeals to your audience.
8. Call-to-action (CTA) copy
The wording of your CTAs can significantly impact their effectiveness. Test different CTA copies to see which ones generate the most clicks or conversions.
For instance, compare “Buy Now” with “Add to Cart” to identify which phrase prompts more visitors to take action. Additionally, you can test the placement, size, and color of your CTA buttons to see how these factors influence user behavior.
Understanding the most effective combination can help you optimize your CTAs for better performance.
9. Forms
Form layout and design can affect completion rates. Test different form layouts or the number of fields to see which ones generate the most completions.
For example, compare a long-form with a short form to determine which one reduces form abandonment and encourages more submissions.
You could also test the impact of optional versus required fields or the inclusion of progress indicators. These variations can help you identify the best form design for minimizing friction and maximizing conversions.
10. Landing pages
Landing page design and content are important for conversions. Test different landing page layouts or content strategies to see which ones perform best.
For example, compare a video landing page with a text-based one to see which format better engages your audience.
Additionally, you can test different headline placements, the inclusion of testimonials, or varying lengths of copy.
These tests will help you determine the most effective elements to include on your landing pages to drive conversions.
11. Email subject lines
Email subject lines are key to open rates. Test different subject lines to see which ones generate the most opens or click-through rates.
For instance, compare a straightforward subject line with a more creative or personalized one. You might also test different lengths, use of emojis, or inclusion of the recipient’s name.
This will help you identify which subject line approaches are most effective in capturing your audience’s attention and encouraging them to engage with your emails.
12. Form designs
The design of your forms can impact conversion rates. Test different form designs, such as a single-page checkout form versus a multi-page form.
Additionally, you could experiment with different styles, colors, and layouts to see which ones are more visually appealing and user-friendly.
This can help you determine which layout reduces form abandonment and encourages more completions, leading to higher conversion rates.
What are the Different Types of A/B testing?
There are different types of A/B tests. Each type has its benefits and drawbacks – this means that the type of testing you choose should depend on your specific goals and circumstances.
Multivariate testing
Multivariate testing is a type of A/B testing that involves testing multiple variations of a webpage or interface with multiple variables changed between them. This type of testing can help you identify the impact of different combinations of changes.
Advantages
- Comprehensive Analysis: Multivariate testing allows you to understand how different elements interact with each other, providing insights into the most effective combinations.
- Detailed Insights: Testing multiple variables simultaneously, helps you pinpoint which specific elements contribute most to the desired outcome.
- Efficiency: This method can save time compared to running multiple separate A/B tests, as it tests several variations at once.
Split testing
Split testing, also known as a split URL test, is a type of A/B testing that involves testing two different web page versions or interfaces with different URLs. This can be useful if you want to test major changes that can’t be made with simple changes to HTML or CSS.
Advantages:
- Major Changes: Split testing is ideal for evaluating significant changes, such as a complete redesign of a webpage, that cannot be implemented with minor HTML or CSS tweaks.
- Isolated Testing Environment: When you use different URLs, you ensure that the tests do not interfere with each other, providing clear and isolated results.
- Scalability: This method allows you to test large-scale changes that might have a significant impact on user behavior.
A/B/n testing
A/B/n testing is a type of A/B testing that involves testing more than two variations of a webpage or interface. This can be useful if you want to test more than two variations of a page or if you have multiple ideas for changes to test.
Advantages
- Diverse Testing: A/B/n testing enables you to test multiple variations simultaneously, providing a broader understanding of potential improvements.
- Comprehensive Comparison: Including more variations, helps you compare a wider range of ideas, helping you identify the best-performing option.
- Increased Optimization: Testing several versions at once increases the likelihood of finding the most effective change.
Bandit testing
Banding testing is a type of A/B testing involving machine learning algorithms to dynamically allocate traffic to web page variations or interface variations based on their performance. This can be useful if you have many variations to test or want to optimize the testing process over time.
Advantages
- Real-Time Optimization: Bandit testing adjusts traffic allocation in real-time, directing more visitors to the better-performing variations as data is collected.
- Efficiency: This method can reduce the time needed to identify the best-performing variation, as it continuously optimizes based on ongoing results.
- Flexibility: Bandit testing is particularly useful for dynamic environments where you need to test and adapt quickly.
Challenges Associated With A/B Testing
While A/B testing is a powerful tool for optimizing websites and applications, it comes with its own set of challenges. Here are five practical challenges you might encounter when conducting A/B tests:
1. Insufficient Sample Size
One of the most common challenges in A/B testing is dealing with an insufficient sample size.
For A/B test results to be statistically significant, you need a sample size that is large enough. If your website or application does not receive enough traffic, the test may take a long time to reach a conclusion, or the results may not be reliable.
This can lead to misleading conclusions, making it difficult to determine if the changes being tested are truly effective.
Businesses with lower traffic volumes often struggle with this. They may need to run tests for extended periods to gather enough data, which can delay decision-making and optimization efforts.
2. Long Testing Duration
Running an A/B test for an adequate period to gather sufficient data can sometimes be a challenge, especially if your business needs to make quick decisions.
Long testing durations can delay the implementation of potentially beneficial changes, causing frustration and slowing down the pace of optimization.
Additionally, during longer test periods, external factors such as market conditions, user behavior shifts, or seasonality can influence the results, complicating the analysis and making it harder to isolate the impact of the tested changes.
3. Implementation Complexity
Implementing A/B tests can be technically complex, especially for significant changes or tests involving multiple variables.
This complexity can arise from altering backend systems, integrating with various analytics tools, or ensuring that the test variations are served correctly without disrupting the user experience.
Implementation errors can lead to inaccurate data, skewed results, and wasted resources.
4. External Influences
External factors, such as seasonal trends, marketing campaigns, or changes in user behavior, can impact the results of your A/B tests.
These factors introduce variability that can skew the results, making it challenging to isolate the effect of the changes being tested.
For instance, a concurrent marketing campaign might temporarily boost traffic and conversions, leading to results that do not accurately reflect the long-term impact of the changes.
This variability can result in misleading conclusions, prompting businesses to implement changes based on data that is not representative of normal user behavior.
5. Analyzing Results
Interpreting the results of an A/B test can be challenging, especially when the data is inconclusive or when multiple metrics show conflicting outcomes.
For example, a change might improve one metric, such as click-through rates, but negatively impact another, like time on site.
This complexity makes it difficult to draw clear conclusions about the overall effectiveness of the test. Additionally, understanding statistical significance and confidence intervals requires a certain level of expertise, which can be a barrier for teams without a strong background in data analysis.
How to Implement an A/B Test using FigPii
We can’t talk about A/B tests without talking about A/B testing tools.
There are hundreds of A/B testing tools in the market, but we recommend FigPii.
You also get access to other conversion optimization tools, such as heatmaps, session recordings, polls, etc., that can help improve your site’s existing conversion rate.
Let me walk you through the process of creating your first A/B test using FigPii.
1. Log in to FigPii.
2. The FigPii code will appear at the bottom section of the dashboard.
3. Click on “copy code.
4. Paste the FigPii Tracking Code into your website’s <head> section.
FigPii integrates with major CMS and e-commerce websites; check our full list of integrations right here.
5. Check your FigPii dashboard to verify the installation.
When the tracking code is installed on your site, the tracking indicator will show you that the code is active.
Once you have added the FigPii Tracking Code to your site, you must wait about an hour to check if it is installed correctly. This usually happens when your site is loaded with the FigPii tracking code installed. But there can be a delay for up to an hour before it shows as “Active”.
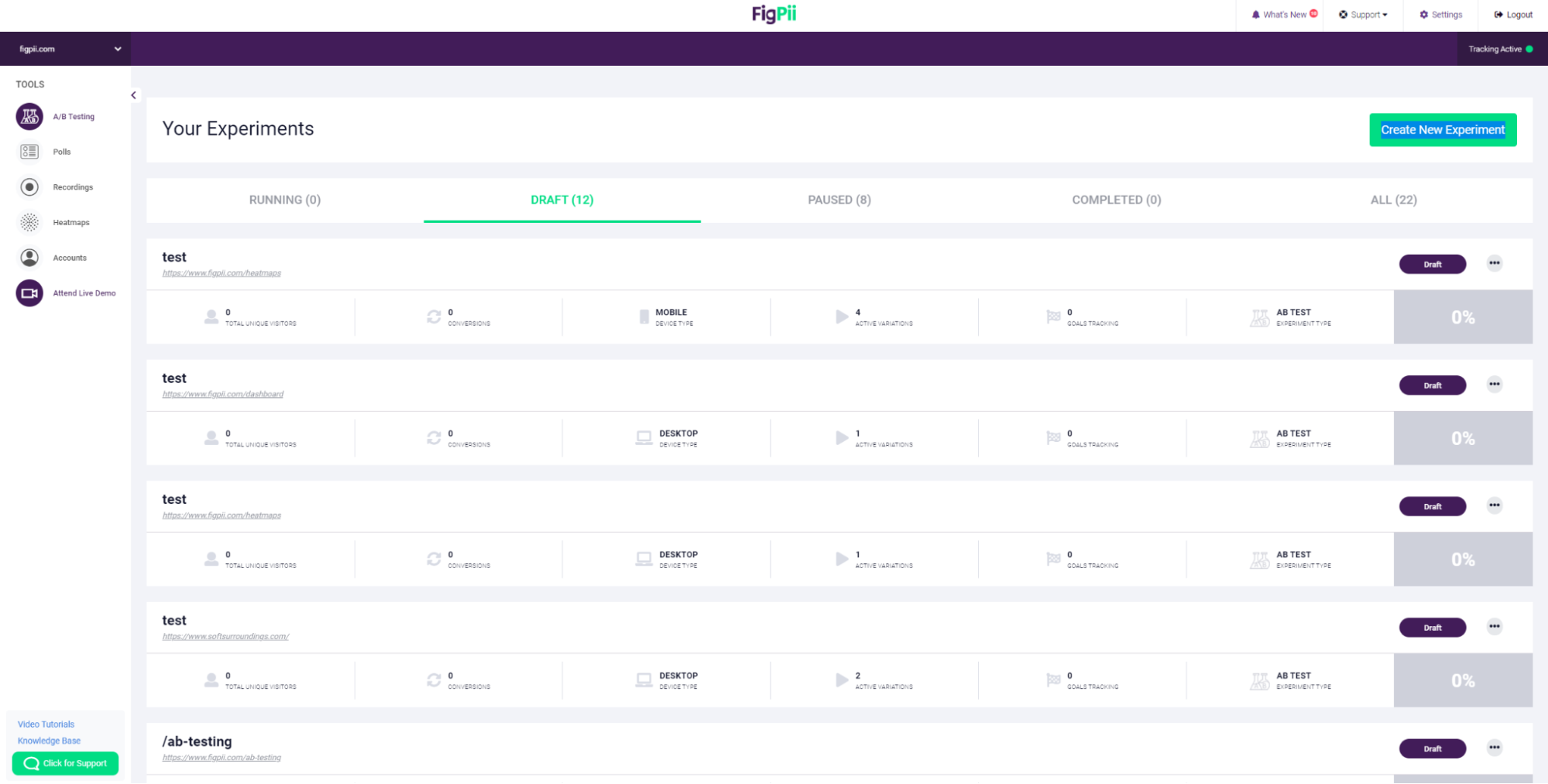
6. log in to FigPii’s dashboard and review the A/B testing section from the side menu.
7. Click on Create New Experiment
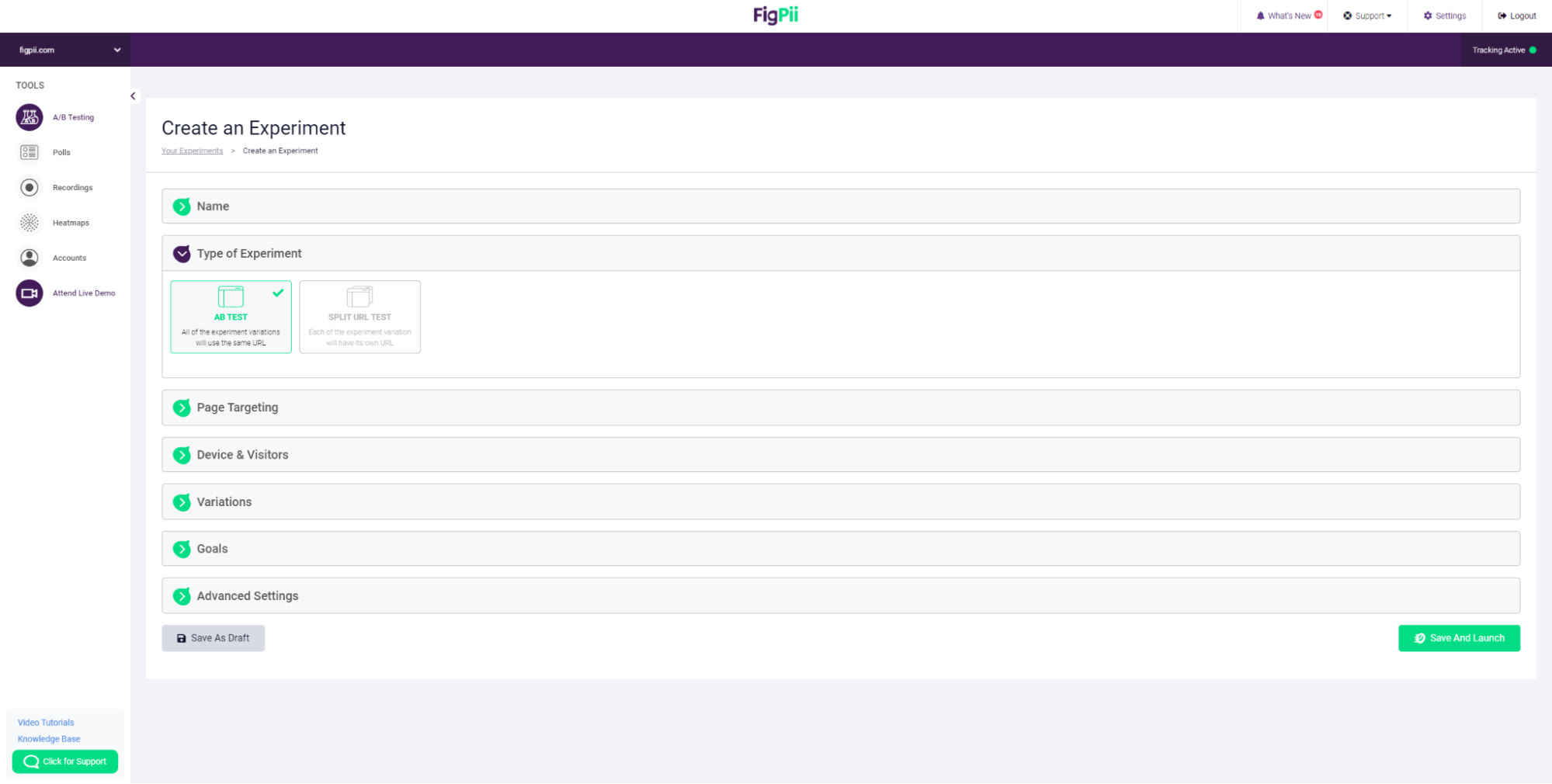
8. Choose your A/B test name
9. Choose whether your experiment is an A/B test or a Split test
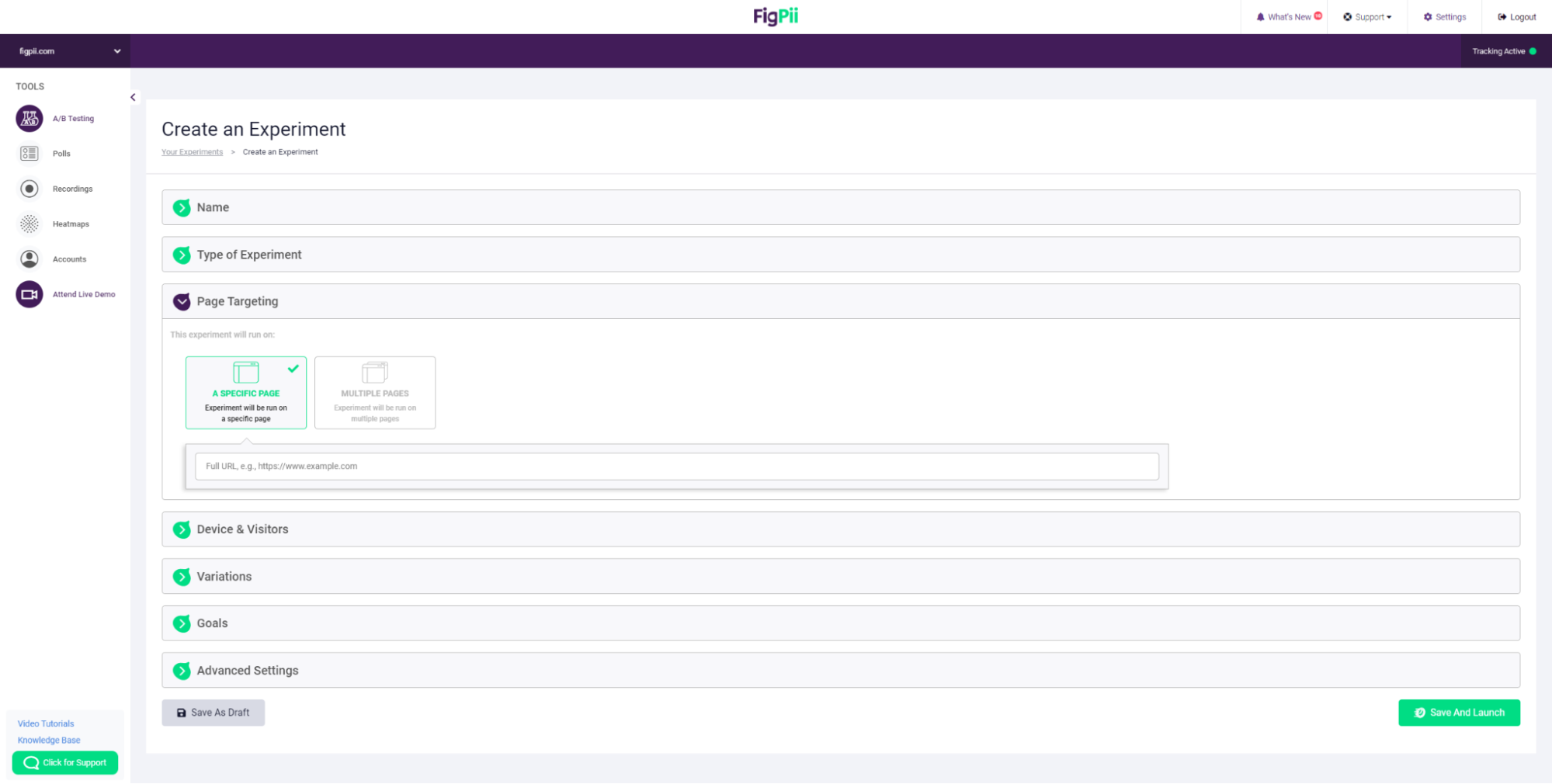
10. Choose whether you want to test just one page or multiple pages
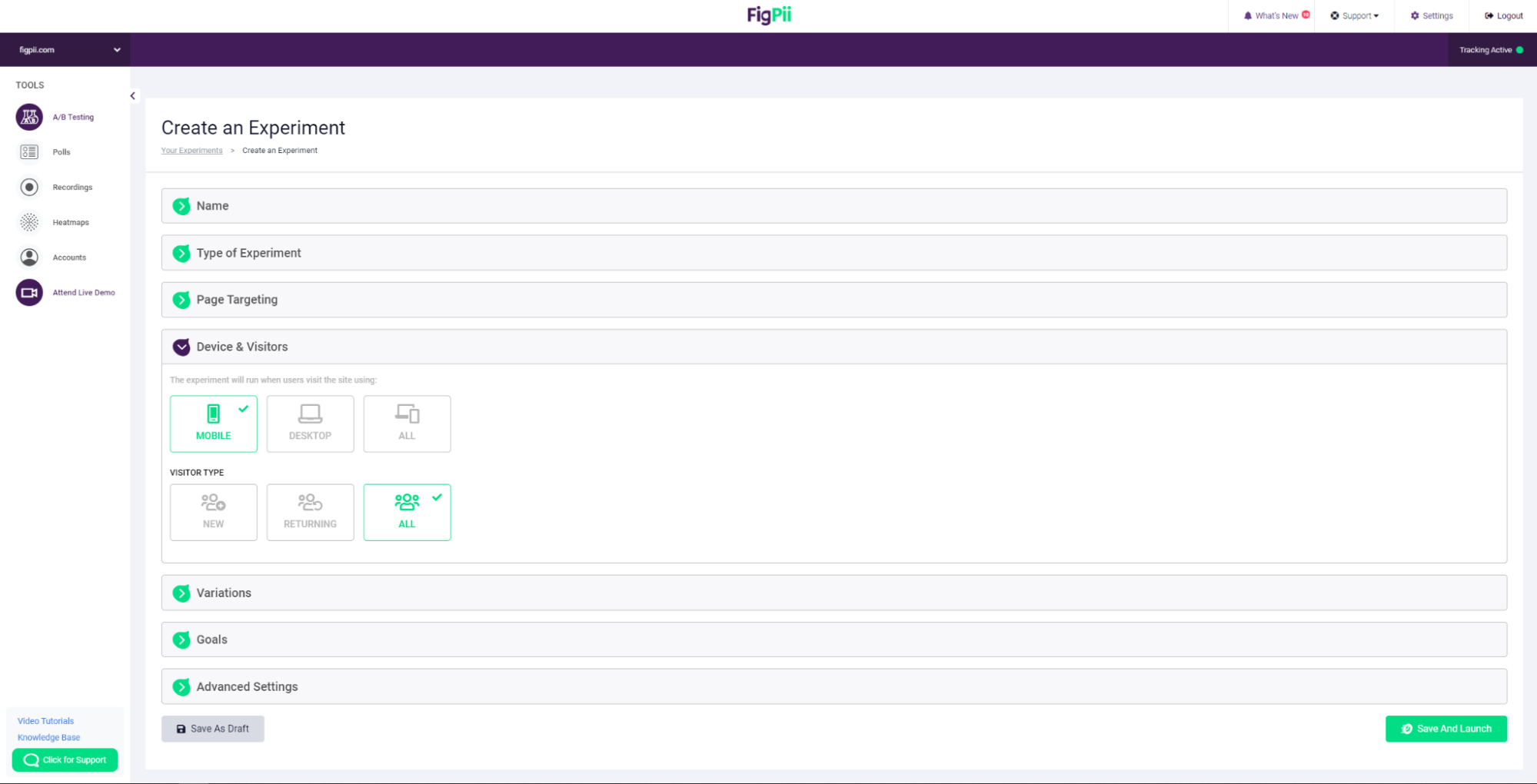
11. You can choose specific parameters to help you design an accurate experiment so you can test things like:
- Which copy converts more visitors to customers?
- Which CTA is getting more clicks
- Did changing these sections make any difference?– And much more
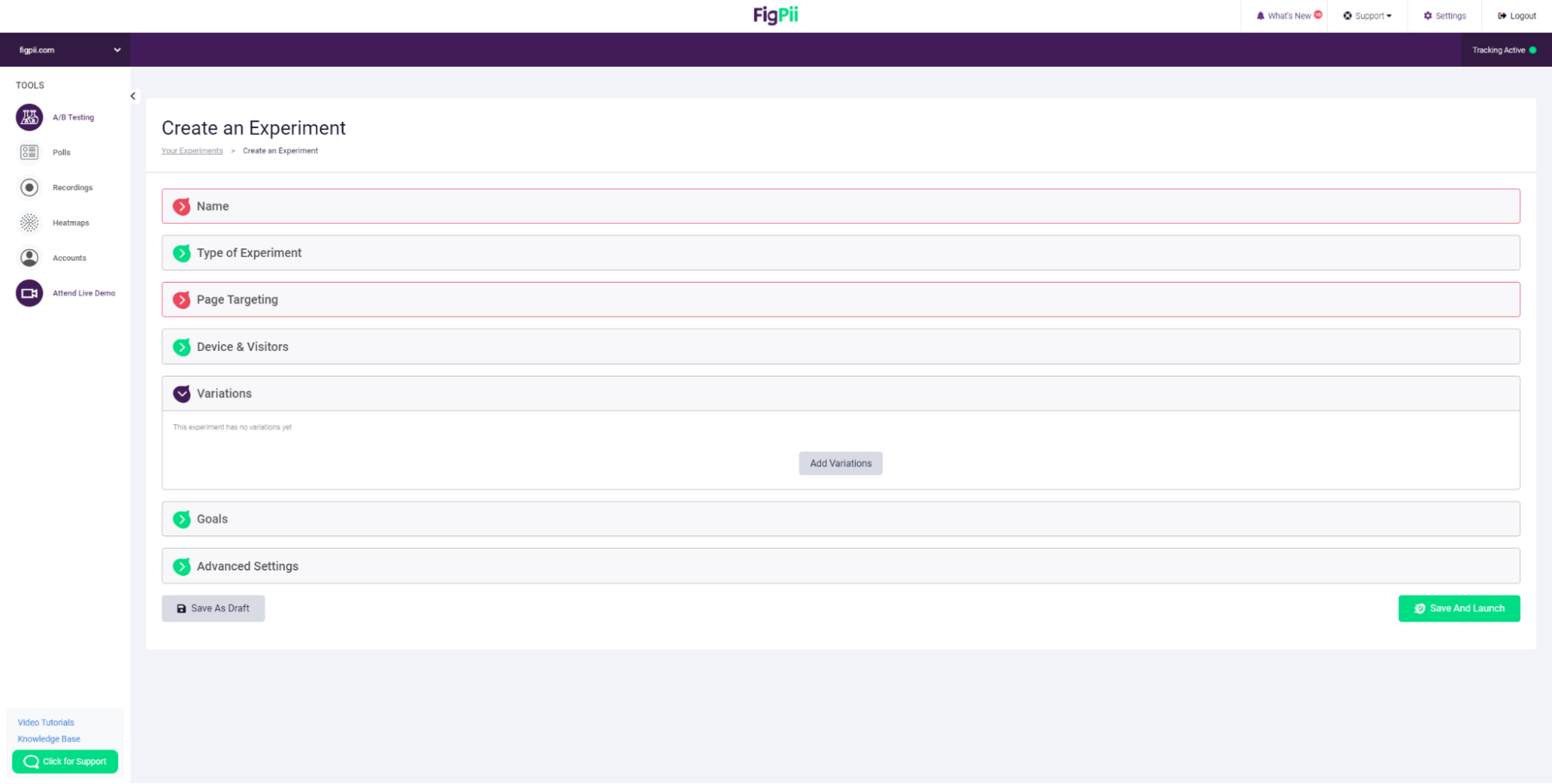
12. Add your first variation, then repeat the step above again to add more variations to the experiment.
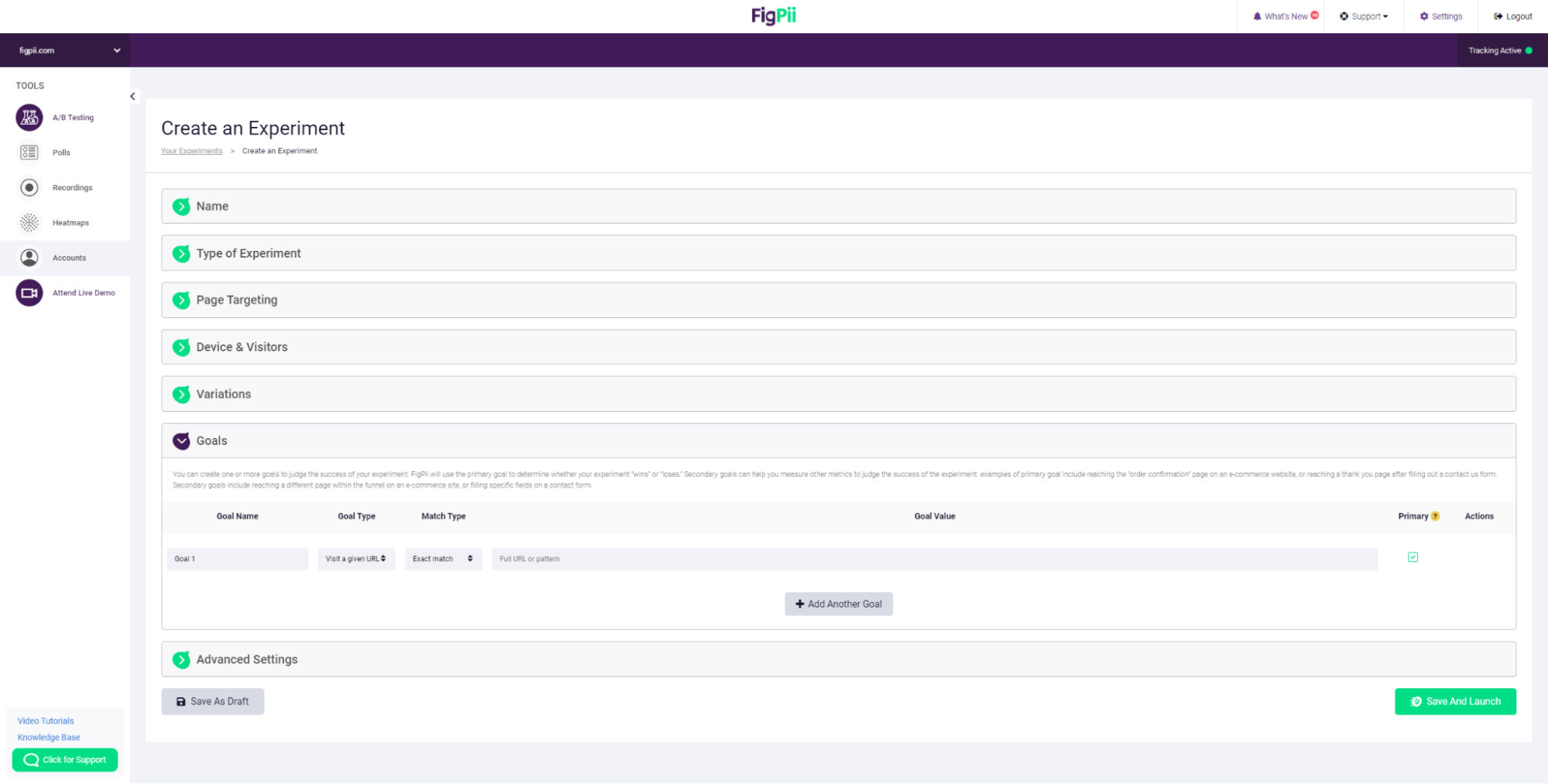
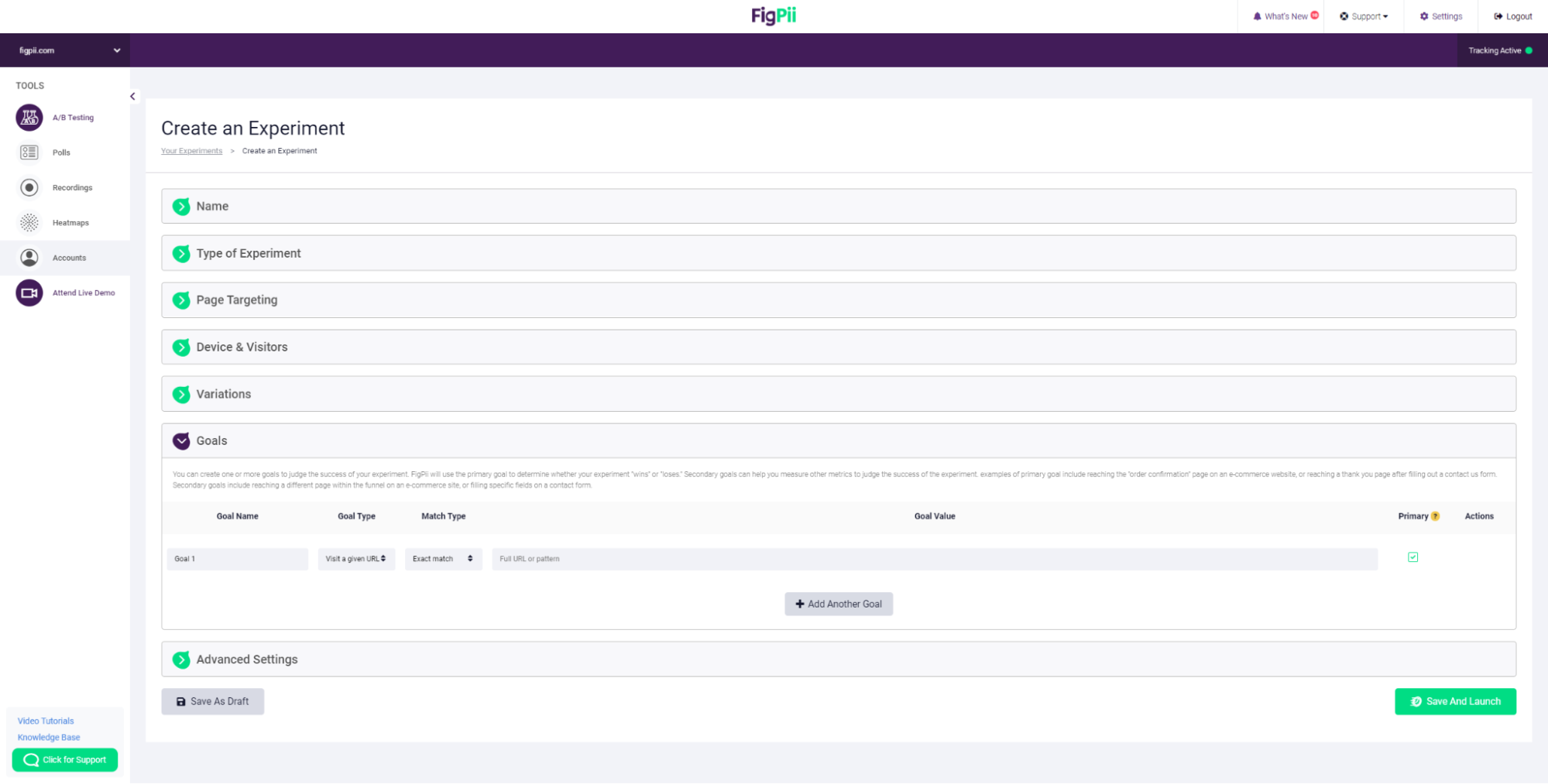
13. Create your goals. You can create one or more goals to judge the success of your experiment.
FigPii will use the primary goal to determine whether your experiment “wins” or “loses.” Secondary goals can help you measure other metrics to judge the success of the experiment.
Examples of primary goals include reaching the “order confirmation” page on an e-commerce website or reaching a thank you page after filling out a Contact Us form.
Secondary goals include reaching a different page within the funnel on an e-commerce site or filling specific fields on a contact form.
14. Refine your experiment using our advanced options to make your experiments more impactful.
15. Setting up the tracking and reporting
Once you have created the variations for your A/B test, the next step is to set up tracking and reporting to measure the performance of your experiment.
This typically involves using a tool, such as Google Analytics, or other analytics tools to track key metrics related to the goal of your A/B test.
Although most A/B testing tools also have features for tracking metrics, it’s recommended to integrate an external tracking tool like Google Analytics.
Integrating an A/B testing tool with Google Analytics can provide several benefits:

- Improved data accuracy: By integrating the two tools, you can more accurately track and measure the impact of your A/B tests on key metrics such as conversions, traffic, and user engagement.
- Enhanced data visualization: A/B testing tools often provide their dashboards and reports. However, integrating with Google Analytics lets you view your test data alongside other important business metrics in a single platform.
- Streamlined data analysis: Integrating your A/B testing tool with Google Analytics allows you to use Google Analytics’ powerful analytics and reporting features to analyze and interpret your test data.
- Increased flexibility: Integration with Google Analytics allows you to use the full range of customization and segmentation options available in the platform to analyze your test data.
And that’s it, and you’re done! You now have an A/B testing experiment. Let it run for a couple of days, and then check the results and which of your variants concluded as winners.
Tips for designing effective A/B Tests
- Quality assurance is a success factor in A/B testing. Before running the tests, QA helps to ensure that your website is functioning as expected and that there are no errors until the tests are over.
- Clearly define the goals of the A/B tests. What are you trying to achieve or improve on your website with the test? This helps you focus on only things that are relevant to your goals.
- Choose the right metrics to measure the success of the test. What are the KPIs that you want to track?
- No matter what you decide to alter or change on different web pages on your site, ensure that, it doesn’t negatively affect the user experience.
- Choose a testing tool with the features required to run your tests effectively. Some features to look out for in A/B testing tools include customer support, multivariate testing, split-URL testing, advanced targeting, revenue impact reports, etc.
Final Thoughts
After conducting an A/B test, future tests, and further analysis may be necessary to understand the reasons for the observed differences and determine if the changes should be implemented permanently.
Combining A/B tests with other optimization techniques, such as user feedback and usability testing, can also improve the quality of the results and help businesses better understand how to improve their products and services.
FAQs on How To Do A/B Testing
What is A/B testing?
A/B testing is a method of comparing two or more versions of a webpage, email, or other digital asset to determine which one performs better. It involves splitting traffic between variations and measuring the impact on a specific metric, such as conversion rates or user engagement.
What is A/B testing in marketing?
A/B testing in marketing refers to experimenting with different versions of marketing materials—such as ads, landing pages, emails, or call-to-action buttons—to identify which version drives better results based on key performance indicators (KPIs).
How to do A/B testing on a website?
To run an A/B test on a website, follow these steps:
-
Define your goal (e.g., increasing conversions or reducing bounce rate).
-
Identify the element to test (e.g., button color, headline, layout).
-
Create variations (A = control, B = variation).
-
Split traffic evenly between versions.
-
Collect and analyze data to determine the better-performing variant.
Is statistical significance an optional part of A/B testing?
No, statistical significance is important in A/B testing. It ensures that the results are not due to random chance but are statistically valid. Without reaching statistical significance, decisions based on test outcomes may be unreliable.
Why do we do A/B testing?
A/B testing helps businesses make data-driven decisions instead of relying on guesswork. It allows for optimizing digital experiences, improving conversion rates, enhancing user engagement, and reducing risks when making changes.